


Wildfires present a significant threat to our palm oil crops, especially during prolonged droughts or El Niño events, leading to substantial financial and environmental impacts, as well as high levels of greenhouse gas emissions. These fires are often ignited by slash-and-burn land clearing practices still employed by some businesses, smallholder farmers, and local communities. Fires originating outside our operational boundaries can quickly spread and encroach upon our areas. Additionally, vegetation fires can occur in the planting areas of our smallholder suppliers, further emphasizing the need for vigilant fire prevention and management strategies across the entire supply chain.
We conduct fire risk assessments based on historical data and perceived vulnerability to identify areas with high fire risk. Based on this assessment, our Ketapang, West Kalimantan (KAL) operation has been designated as a priority for fire prevention and management. However, ongoing demographic and economic growth, coupled with global warming, increases the risk of fire in other operations, such as ANJAS, followed by PPM, PMP, ANJAP, SMM and ANJA, in order of risk level.
Based on the results of our fire risk assessment, we have developed an Integrated Fire Management (IFM) system, which is a cross-departmental and fully integrated approach encompassing prevention, mitigation, preparedness, early detection action, and response. As forest fires are most commonly caused by human activities, our primary focus is on prevention and mitigation strategies. To this end, we conduct community socialization efforts to raise awareness about fire safety and risks. Additionally, we invest in community development initiatives to transition people away from slash-and-burn farming practices, aiming to minimize the occurrence of uncontrolled forest fires, particularly during drought seasons.
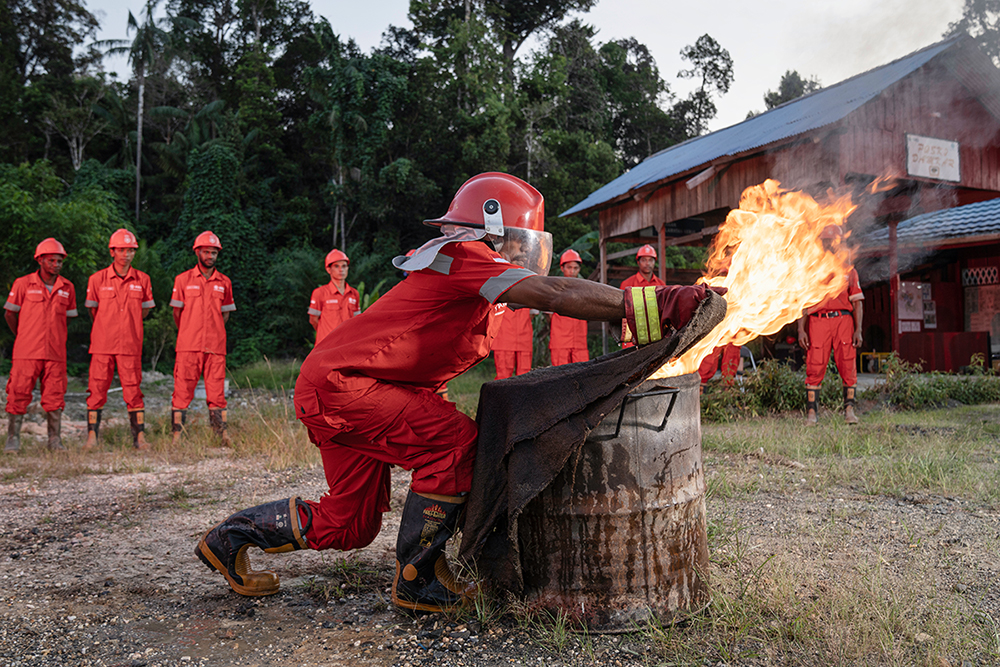
For early identification of fire hotspots, we utilize satellite-based monitoring, complemented by local monitoring through fire towers and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). The Integrated Fire Management (IFM) system not only monitors hotspots but also provides daily, weekly, and monthly fire hotspot prediction reports to our estates. As part of our fire preparedness measures, we maintain a fully trained Rapid Response team on standby to address fire occurrences when fire warnings are detected. Additionally, we have established an incident management team (IMT), which is activated as soon as an issue is reported, ensuring a swift and coordinated response to fire incidents.
To complement this, we also have firefighting systems installed across all our estates. Each location is not only furnished with its own team of trained and professional firefighters, but also with a range of specialized equipment including fire engines, and portable water pumps. Some specific estates also have rubber boats for rapid and efficient response capabilities. Moreover, ANJ adheres to stringent safety standards for all firefighting gear, ensuring the safety of both our personnel and the communities we serve. In line with our commitment to community welfare, our firefighting capabilities and resources often extend beyond our premises, assisting in combating flooding and other emergencies in surrounding communities, showcasing ANJ’s dedication as a responsible community partner.
To ensure the sustainability of our fire management measures, we actively involve stakeholders and local communities in the process. This involvement is facilitated through the smallholder farmer firefighting groups (Kelompok Tani Peduli Api/KTPA) and the Desa Mandiri programs, which offer financial incentives to villages that implement fire prevention and management efforts. Additionally, we collaborate with local authorities, communities, and law enforcement agencies, including police and military forces, as well as local fire brigades that have received specialized training from the Ministry of Environment and Forestry’s Manggala Agni trained forest fire brigade. This comprehensive approach ensures coordinated and effective fire management, with the support and participation of the broader community.
Throughout 2023, the RSPO Fire Watch detected 22 hotspots inside our concessions (Cultivation Rights Title or HGU), namely three at PT Sahabat Mewah dan Makmur (SMM), one at PT Permata Putera Mandiri (PPM) and 18 at PT Galempa Sejahtera Bersama (GSB). However, our field verification at GSB found that 17 hotspots at GSB occurred on uncompensated land of local communities inside our concession and one hotspot actual location was outside our concession. The boundaries of our estates in GSB are not yet defined as the land compensation program is still ongoing.
Meanwhile, our satellite monitoring detected four hotspots with a normal confidence level inside our concession in SMM and 41 hotspots on uncompensated land of local communities inside our concession in GSB. The collaboration of our firefighting team, KTPA and relevant stakeholders promptly extinguished the hotspots, therefore no wildfire incidents occurred in 2023. We continue to engage with local communities on wildfire prevention initiatives.
Prolonged drought significantly increases the risk of forest fires, posing a substantial threat to ecosystems and communities. Despite these challenges, ANJ has successfully prevented forest fires within our areas in 2023. Our comprehensive strategy, which integrates technical mitigation measures, community empowerment initiatives, and data-driven monitoring, has been instrumental in effectively addressing and mitigating this threat. Even amidst projections indicating a potential increase in the intensity of the current El Niño in the future, we remain hopeful that we can persist in operating our business while safeguarding our natural resources.
